The extension can import only xls files, is not compatible with the new xlsx Office format
Excel connection:
The ADO connection string to connect to a excel file. The predefined value is compatible with IIS and Windows operating system, for other operating system you must change this string. The string contain 2 variable value:
#DBQ# - the full path of the excel file
#DefaultDir# - The folder of the excel file
The extension will replace this 2 string with the imported excel file value.
Import on:
On Page Load
on the OnLoad event of the page
Post variable
when the request.form variable exists
Get variable
when the request.querystring variable exists
Request variable
when the generic request variable exists
Session variable
when the session variable exists
Application variable
when the Application variable exists
Cookie variable
when the request.Cookie variable exists
Progress bar:
The progress bar you want see during the import process
Progress update:
The number of imported records between each progress update
Redirect page:
The page you want redirect after the import process is end
Display errors:
If checked after the import process is end and if there are errors, display a table with the list of errors, the SqlQuery and the line number.
File path:
The file path of the Excel file you want import from. The path must be relative to a file inside the site root or in a folder. Normally the user must upload the file Excel so you must create an upload page with your standard upload method where the user can upload a Excel file in a folder inside your site. The upload file must have the same name you setup in this field and all the time the user want import from Excel file must upload a file with this name or you can setup the upload page to change the name of the uploaded file and give all the times the same name.
Range name:
You can store data in a Microsoft Excel Spreadsheet and then use this extension to extract the infromation. The spreadsheet acts like a database. The process is fairly simple and I will break it down into 2 steps:
STEP-1: Create an Excel Spreadsheet
Open Excel and create a spreadsheet that looks like this:
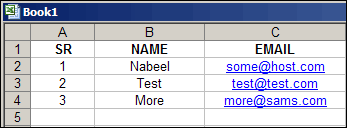
In this sheet the SR, NAME and EMAIL are the column names.
STEP-2: Define named ranges in the spreadsheet
Now that we have created a spreadsheet, its time to define a named range within Excel that will be treated as a table for our extension import process.
To create a named range, select all the fields that have data in them, with the column names, then go to INSERT > Name > Define... > Type in ImportRange > Press OK > Save your file
Now that we have the excel file and the named range in place, we can start working with the extension
Db format date:
This is the format of the date field your database required. When you import a date field The extension get the string value from the Xml file and transform in a date variable, after with the Db format date create a new date string with the exact format your database need.
Db format boolean:
This is the format of the boolean field your database required. When you import a boolean field The extension get the string value from the Xml file and transform in a boolean variable, after with the Db format boolean create a new boolean string with the exact format your database need.
Date delim char:
When you import a date value into the database the SqlQuery must have a field delimiter and this delimiter depend on the DataBase you use.
For. example with MsAccess the delimiter must be # and the date syntax must be like #01/01/2006#, but with SqlServer the delimiter must be a ' and the date syntax must be like '01/01/2006'
Date null:
The value you must use into the SqlQuery to insert a date with a null value, when the date value is void.
Normally is used the Null but in some case you must use the ''
This value depend on the database setup
String null:
The value you must use into the SqlQuery to insert a string with a null value, when the string value is void.
Normally is used the Null but in some case you must use the ''
This value depend on the database setup
Number null:
The value you must use into the SqlQuery to insert a number with a null value, when the number value is void.
Normally is used the 0 (zero) but in some case you must use the Null
This value depend on what you prefer have in your database if a null field or a field with 0 (zero) value.
Connection:
In the Connection pop-up menu, select a connection to the database.
Click the Define button if you need to define a connection
Data base table:
In the Data Base Table pop-up menu, select the database table into which the record should be inserted
Unique column key:
(for the database table)
In the Unique Key Column pop-up menus, select a key column (usually the record ID column) to identify the record in the database table. Select the Numeric option if the value is a number. A key column usually accepts only numeric values, but sometimes it accepts text values.
Fields panel
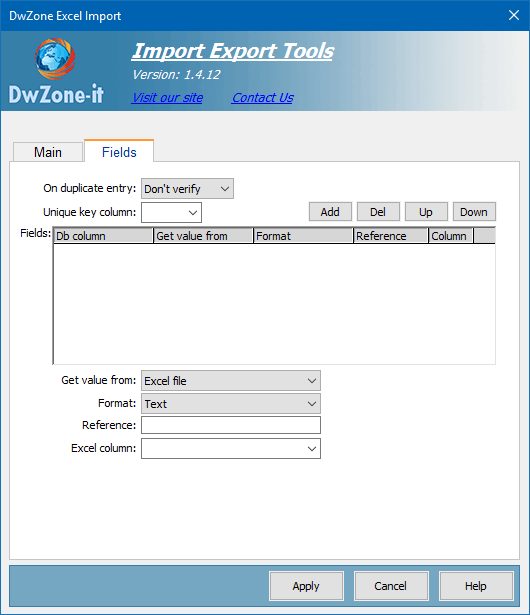
On duplicate entry:
The available value are:
Don't verify
In this case the extension don't verify if there are duplicated record, but insert all the records
Skip
The record is not inserted and the extension skip the record.
Update
The extension update the record with the value from the import Xml file.
Throw error
Generate an error and the record is not inserted and not updated. This error will be displayed after the end of the import process and only if the Display errors is checked.
Unique column key:
(for the Excel file)
In this combo you must select the Excel column number that is the unique column key value of the record and is used to determine if the record exist in the table.
To determine if a record exist the extension search in the table if there is a record where the Unique Column Key for the Database and the Unique Column Key for the Xml file are equal.
This field cannot be imported into the database because normally this value is assegned from the database each time you add a new record and also cannot be updated.
Fields:
After you select the table where insert the record this element display the list of table field with a predefined GetFrom, Format and Reference.
It's possible personalize all this parameters like you need, you must select a field in this element and in the 3 element belowe you can modify the GetFrom, Format and Reference..
With the 4 button in the right you can remove (Del button) the field you don't want export or add (Add button) a field you have deleted and setup the order position for each field with the button Up and Down button. The position of the fields don't have any importance from the import process.
Db column:
The DataBase field name, not modificable
Get value from:
This combo define where get the value for each database fields.
Normally you get the value from the Xml file but may be for some fields you need get the value from other source like session variable, application variable, cookie variable, parameter send with querystring or with a form or also entered value.
Format:
The format of the exported data.
The available format are:
Text
Numeric (Integer)
Numeric (.)
Numeric (,)
Data
Boolean (true,false)
Boolean (1,0)
Boolean (-1,0)
Boolean (Y,N)
Boolean (Yes,No)
There are 2 format need more info: Numeric (.) and Numeric (,), the first is a number with the . (comma) decimal separator like 12345.67 and the second is a number with a , (virgola) decimal separator like 12345,67
In the SqlQuery all the number with decimal value must be inserted with the point decimal separator and without the GroupDigit separator, and you must choose the format for the number valur you receive from the Xml file so the extension will format the value in the exact format the SqlQuery need.
Reference:
Define the name of the refenced Xml node/attribute or the name of the session,application variable from where get the value for the field.
If the reference is not find will insert a null value in the record.
Excel column number:
Define which column of the Excel file contain the value for the selected field. For example in this image the NAME is the column 2, etc...


